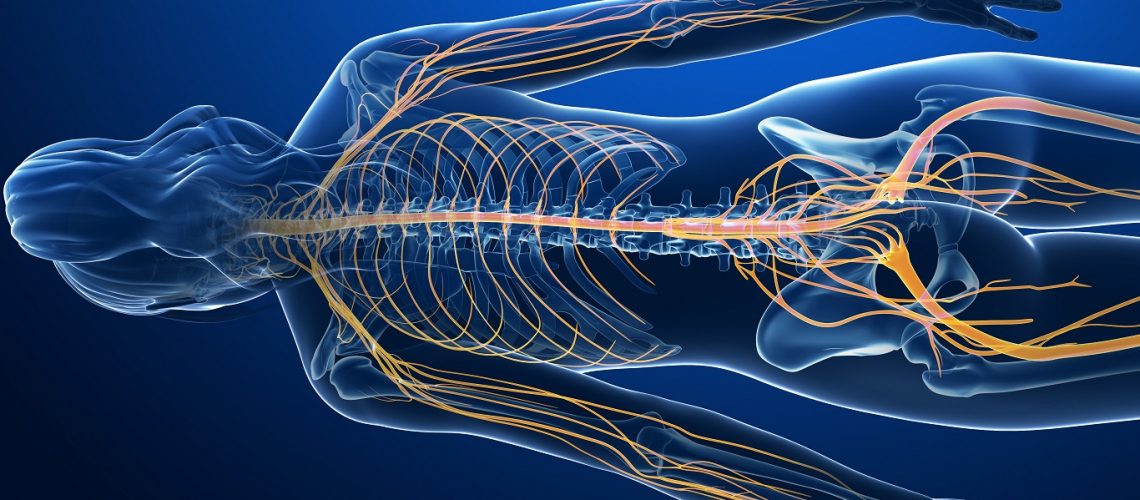
There appears to be some confusion and misinformation about Ketamine even among health care practitioners. This may be due to so much controversial, sometimes false information, disseminated through the media and made accessible due to advances in information and communication technology.
Yet, multiple well-structured, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, peer-reviewed studies have been done and published on the use of Ketamine in various strengths, forms of administration and therapeutic purposes over the past years. These studies present both the positive and negative results related to the use of Ketamine.
Our focus is to present the information concluded from studies analyzing only transdermal use of Ketamine in pain management formulations.
Sys¬temic ketamine has not gained popularity as an analgesic compound. This is due to its limited usage as an anesthetic and its potential for addiction and dependence.
Topical administration of ketamine however, has been demonstrated to be devoid of serious side effects, and thus can be used in the management of various pain states such as neuropathic pain and complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS). Despite using high concentrations of topical ketamine, clinically significant side effects are rare.
The existing literature supports the topical use of Ketamine for several types of pain: neuropathic, spinal, local, surgical, etc. as a viable treatment option.
When compounded in combination with other active pharmaceutical ingredients (API’s), Ketamine has also been proven to be effective in transdermal pain preparations – including creams, gels or ointments – it has the realistic potential to help many patients who suffer from pain, particularly patients experiencing chronic pain with a neurogenic component to it.
The efficacy of topical preparations containing Ketamine is based on the nociceptive and neuropathic pain blocking property of Ketamine. Topical administration reduces the pill burden and increases patient compliance and adherence to medications. Ketamine is a noncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonist with opioid activity. Its analgesic effects rely on glutamate receptor activity, voltage-sensitive calcium channel blockage, interference with opioid receptors, and cholinergic and monoaminergic functions.
Chronic neuropathic pain, often presented as diabetic neuropathy, appears to be the major indication for transdermal use of Ketamine in compounded medications containing other synergistically acting API’s.
Neuropathic pain is often resistant to conventional analgesics such as NSAID’s and opioids, so clinicians must use adjuvants such as tricyclic antidepressants (TCA), anticonvulsants, local anesthetics and corticosteroids to achieve the desired effect.
In recent years, a better understanding of the underlying pathophysiology of neuropathic pain led researchers to clarify and appreciate some of the mechanisms of action of Ketamine for their therapeutic value in transdermal formulations used for the treatment of chronic neuropathic pain. Apparently central sensitization, where receptors such as NMDA, AMPA and M-glu play a key role, perpetuates chronic neuropathic pain even when peripheral sensory input is absent. This is thought to cause allodynia, hyperalgesia and hyperpathia. Ketamine is thought to help patients with chronic neuropathic pain due to its NMDA receptor activity and its peripheral action at both opioid and Sodium/Potassium channels.
If you are a health care practitioner that sees patients with chronic neuropathic pain, you should seriously consider using compounded formulations containing Ketamine to help them.
If you’d like to learn more about the transdermal use of Ketamine, supporting literature, and how to prescribe the compounded formulations containing Ketamine, we recommend you work collaboratively with a reliable and experienced compounding pharmacy.
Let HALDEY Pharmaceutical Compounding be your choice compounding pharmacy. Contact one of our expert compounding pharmacists today to answer any questions you may have with regards to Ketamine and pain management formulations. You will be one phone call away from being able to provide safer, more effective, and customized transdermal pain medications for your patients.
References:
Petrenko AB, Yamakura T, Baba H, Shimoji K. The role of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors in pain: a review. Anesth Analg. 2003 Oct;97(4):1108-16.
Wu LJ, Zhuo M. Targeting the NMDA receptor subunit NR2B for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Neurotherapeutics. 2009 Oct;6(4):693-702. doi: 10.1016/j.nurt.2009.07.008.
Chizh BA, Headley PM. NMDA antagonists and neuropathic pain–multiple drug targets and multiple uses. Curr Pharm Des. 2005;11(23):2977-94
https://www.diabeteseducator.org/news/aade-blog/aade-blog-details/karen-kemmis-pt-dpt-ms-cde-faade/2017/07/26/the-2017-national-diabetes-statistics-report-is-here
https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/data/statistics/statistics-report.html
https://www.gstatic.com/healthricherkp/pdf/diabetic_neuropathy.pdf
Lynch ME, Clark AJ, Sawynok J, Sullivan MJ. Topical 2% amitriptyline and 1% ketamine in neuropathic pain syndromes: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Anesthesiology. 2005 Jul;103(1):140-6.
Barton DL, Wos EJ, et al. A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of a topical treatment for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: NCCTG trial N06CA. Support Care Cancer. 2011 Jun;19(6):833-41. doi: 10.1007/s00520- 010-0911-0. Epub 2010 May 25
Mazières B, Rouanet S, Guillon Y, Scarsi C, Reiner V. Topical ketoprofen patch in the treatment of tendinitis: a randomized, double blind, placebo controlled study. J Rheumatol. 2005